Understanding U-Value: A Simple Guide for Homeowners Buying Windows and Doors
If you're buying new windows or doors for your home, you've probably come across the term "U-value." It may sound technical, but it's one of the most important factors to consider when choosing energy-efficient products. In this guide, we'll explain what U-value means, why it matters, and how to use it to make informed decisions when buying windows and doors.
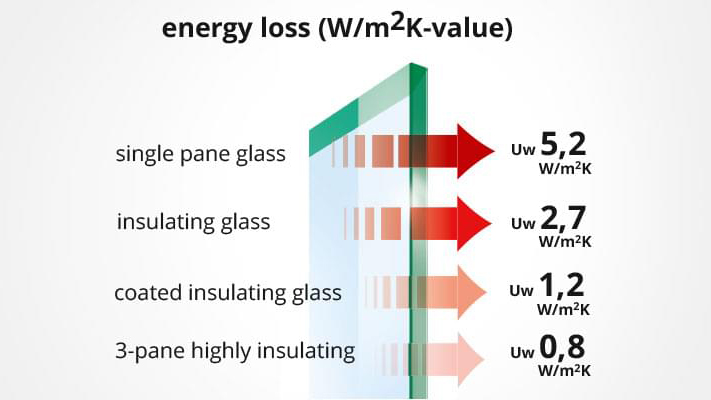
U Value Examples
What Is U-Value?
U-value, also known as thermal transmittance, measures how well a building element (like a window or door) conducts heat. In simple terms, it tells you how much heat is lost through a material. The lower the U-value, the better the insulation. A product with a low U-value will keep more heat inside your home, helping you save energy and stay warm during colder months.
U-value is measured in units of W/m²K (watts per square metre per degree Kelvin). This unit indicates how many watts of heat pass through one square metre of material for every degree difference in temperature between inside and outside. The key thing to remember is: lower U-values mean better thermal performance.
Why U-Value Matters for Homeowners
Windows and doors are major sources of heat loss in most homes. Even with insulated walls and lofts, poor-quality glazing can lead to cold drafts, condensation, and high energy bills. By choosing products with better U-values, you can:
- Improve your home's energy efficiency
- Lower your heating and cooling costs
- Increase indoor comfort all year round
- Reduce your carbon footprint
- Add value to your property
With energy prices on the rise, understanding U-values is not just a technical detail—it's a smart investment in the long-term performance of your home.
What Is a Good U-Value for Windows and Doors?
In the UK, Building Regulations set minimum energy performance standards for new and replacement windows and doors. As of the most recent update, the required maximum U-values are:
- Windows: 1.4 W/m²K or better
- Doors (glazed): 1.4 W/m²K or better
- Doors (solid): 1.0 W/m²K or better
However, many modern window and door systems exceed these minimum requirements. Triple glazed units, for example, can achieve U-values as low as 0.8 W/m²K or better, offering superior insulation. For Passivhaus and ultra-low-energy homes, even lower values may be targeted.
Factors That Affect U-Value
The U-value of a window or door is influenced by several components, including:
1. Glass Type: Double glazing with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings can significantly reduce heat loss. Triple glazing adds another layer of insulation, further improving performance.
2. Gas Fill: Inert gases like argon, krypton, or xenon are often used between the panes of glass to slow down heat transfer.
3. Spacer Bars: These separate the panes of glass and can be made from metal or warm-edge materials. Warm-edge spacers reduce thermal bridging.
4. Frame Material: uPVC, timber, and thermally broken aluminium frames each have different insulating properties. High-quality frame design is essential to achieve good U-values.
5. Overall Construction: The U-value provided by manufacturers is usually for the whole window or door unit, not just the glass. It includes the frame, glazing, and spacers together as a single system.
How to Read U-Value Ratings
When comparing window or door options, always look for the whole-unit U-value, not just the centre-pane U-value. Centre-pane values only measure the performance of the glass itself, while whole-unit values account for the frame and edges too. A window might have an excellent centre-pane U-value but perform poorly overall due to frame heat loss.
Reputable manufacturers will list the whole-unit U-value on product labels or technical datasheets. Some may also display energy ratings based on U-value and other factors such as solar gain and air leakage. In the UK, this is often represented by the British Fenestration Rating Council (BFRC) scale from A++ to G.
How to Improve U-Value in Your Home
If you're planning to upgrade your windows and doors, here are some ways to get better U-values and maximise energy efficiency:
- Choose double or triple glazing with Low-E coatings
- Look for units with argon or krypton gas fill
- Select warm-edge spacer bars
- Pick high-quality, thermally efficient frame materials
- Work with FENSA-registered installers for compliance and quality assurance
Upgrading your glazing can also improve airtightness and reduce drafts, further enhancing the comfort and efficiency of your home.
U-Value vs R-Value: What's the Difference?
U-value is the European standard for measuring thermal performance, while R-value is used more commonly in North America. The two are inversely related: the higher the R-value, the lower the U-value. Specifically, R = 1/U.
For example, a window with a U-value of 1.0 W/m²K has an R-value of 1.0. A lower U-value of 0.5 W/m²K would have an R-value of 2.0, indicating better insulation. Although they represent the same concept, it's important to use the correct standard for your region when comparing products.
Frequently Asked Questions About U-Value
Do all double glazed windows have the same U-value? No, U-values vary depending on glass type, gas fill, spacer bars, and frame material. Not all double glazing is equal, so it’s worth checking the product specification.
Is triple glazing always better than double glazing? Triple glazing can offer lower U-values, but it’s not always necessary for every home. Factors like cost, weight, and location play a role in determining the best option.
Can I measure U-value myself? Not accurately. U-value testing requires specialised equipment and standards. Always rely on certified product data from manufacturers or accredited installers.
Does a lower U-value mean more savings? Generally yes—lower U-values help reduce heat loss and improve efficiency, but actual savings depend on the size of your glazing, insulation elsewhere in the home, and your energy use habits.
Conclusion: Make U-Value Part of Your Buying Decision
U-value is a key indicator of how well your windows and doors will perform when it comes to heat retention and energy efficiency. By understanding what it means and how it works, you can make smarter, more informed choices when upgrading your home.
Look for products with certified low U-values, whole-unit performance ratings, and high-quality construction. Whether you're renovating or building new, choosing energy-efficient windows and doors can help you stay warm, save money, and create a more comfortable living environment for years to come.













Great post! Glazing is such an important aspect of both aesthetics and energy efficiency in modern buildings. It’s amazing how the right glass choices can completely transform a space while also improving insulation and reducing noise. Thanks for sharing!